Defining Default LLM Models
To further simplify the management of LLM models, GPT Mates allows you to define default logical models for each type of Mate (Native, Assistant, Web Search, Image Generation). This ensures that newly created or onboarded Mates automatically use the most appropriate models, while still giving you the flexibility to customize individual Mates as needed.
Here’s how to define default LLM models:
- Access Organization Settings:
- Click on the black downward arrow next to your organization's name at the top left of the screen.
- Select "Settings" from the drop-down menu.
- Navigate to the "Models management" Tab:
- Go to the "Models management" tab to manage the connections and models for your Mates.
- Go to the "Default models" Tab:
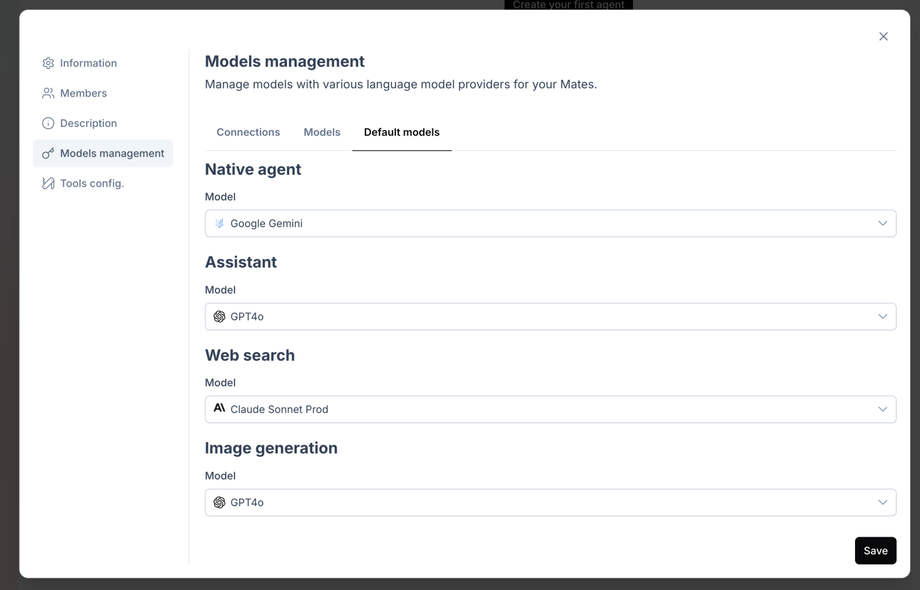
- Select the "Default models" tab within the "Models management" section.
- Define Default Models by Mate Type:
- For each type of Mate (Native agent, Assistant, Web search, Image generation), choose a default logical model from the dropdown menu.
- The dropdown menu will only show compatible logical models, filtered for each Mate type.
- Save Changes:
When you change a default model, all Mates using that default model will automatically be updated to use the new model. However, you can still customize a Mate's model by going to the Mate's profile. This is useful when you want to test a new model in your Mates before making the change available to everyone.
Importance of This Action
Defining default LLM models simplifies the management of models assigned to Mates while optimizing their performance. By mixing several providers, you benefit from the specific advantages of each, thereby improving the flexibility and efficiency of the Mates. For example, if a new LLM model is launched by a provider and the organization wants to use it, simply set it as the default model for a Mate type, and all Mates using this default model will automatically switch to the new provider’s model.